Medical devices
search
news
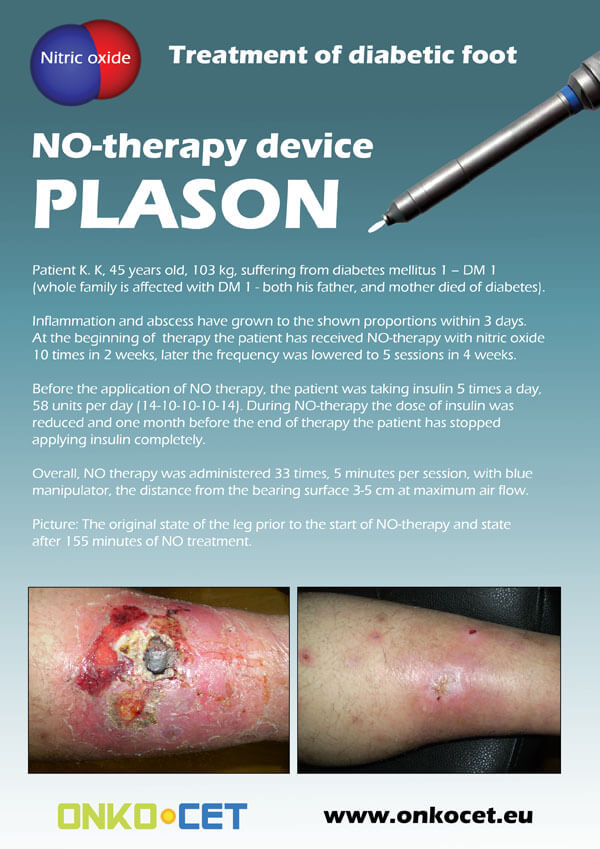
The PDF with the short report with pictures from the therapy of a diabetic foot can be viewed or downloaded here.
The pictures from the treatment of unhealing wounds an be found here:
http://www.onkocet.eu/en/produkty-detail/220/1/
The pictures from the treatment of unhealing wounds an be found here:
http://www.onkocet.eu/en/produkty-detail/293/1/
ONKOCET Ltd. has exhibited the devices from its portfolio on the MEDTEC UK exhibition in Birmingham, April 2011 through our partner Medical & Partners.

 The ONKOCET company has successfully reached the certification of yet another medical device, Infrared Camera SVIT. The Certificate can be found here. The videos from the device operation can be found here.
The ONKOCET company has successfully reached the certification of yet another medical device, Infrared Camera SVIT. The Certificate can be found here. The videos from the device operation can be found here. Our device, the non-invasive blood analyzer AMP has won the Golden Incheba prize at a medical exhibition SLOVMEDICA - NON-HANDICAP 2010. A big thank you goes to the organizers of the exhibition for acknowledging the quality of our device and to the exhibitor, the Medical & Partners company, for introduction of the AMP device to the medical public again.
Our device, the non-invasive blood analyzer AMP has won the Golden Incheba prize at a medical exhibition SLOVMEDICA - NON-HANDICAP 2010. A big thank you goes to the organizers of the exhibition for acknowledging the quality of our device and to the exhibitor, the Medical & Partners company, for introduction of the AMP device to the medical public again.We are pleased to inform our business partners, that our company has succesfully finished the certification process of Concor Soft Contact Lenses.
 You can find the certificate here.
You can find the certificate here.More information on Concor Soft Contact Lenses go to section Medical preparations/Concor soft contact lenses, or follow this link.
 Our company has finished the certification process for another medical device, computerized spirometer MAS-1K with oximeter. You can find the device certificate here.
Our company has finished the certification process for another medical device, computerized spirometer MAS-1K with oximeter. You can find the device certificate here..jpg) Since May 2010 there is a new version of AMP device available.
Since May 2010 there is a new version of AMP device available.Follow this link if you want to see the pictures and specifications of the device.
http://www.onkocet.eu/en/produkty-detail/293/1/
 Dear partners,
Dear partners, In October 2009 we have received CE certificate for another device from our portfolio, NO therapeutical device PLASON. You can find more information about this revolutionary device, used for healing of unhealing wounds, diabetic foot, or for cosmetical purposes, at our webpage, section "Medical devices" -> PLASON-NO Therapy.
.gif)
Best regards
Team of ONKOCET Ltd. company
NO and cellular cultures (experiment)
Action exogenous NO on the cellular cultures of fibroblasts and cells of neuron
The ability of the NO- containing gas flow (NO -CGF) to accelerate wound healing requires the study of the mechanisms of this effect. Morphological data speak about the acceleration of the proliferation of fibroblasts, endotheliocyte and epithelial cells, synthesis of collagen. However, a question about that remains open, does act exogenous NO on multiplication and functions of fibroblasts directly or is only defined by example - through the normalization of microcirculation, the activation of cytokine and etc.
The fibroblasts of the skin of man and the transformed glial cells of neuron of the Gasser's unit of the rat (NGUC 1) interwove in the plastic Petri dishes (diameter of 30 mm) and cultivated in environment RPMI 1640 and DMEM with 10% embryonic calf serum respectively to the state of dense monolayer. Then cups with the culture of cells were processed:
1) NO -CGF of apparatus "PLASON", which contain 300 ppm of the nitrogen oxide;
2) by the gas mixture of nitrogen and NO from the balloon with the analogous NO content;
3) by the air flow without NO (control). The time of action - 5, 10, 15 and 20 sec, on 4 Petri dishes to each temporary point. In all it is carried out 3 sets of experiments with the different passages of cells. Influence of exogenous NO on the synthesis DNA and protein was evaluated according to the start of C14 - thymidine in DNA and C14 - amino acids in proteins with their synthesis in the cultivated cells the hour after their working. The time of labelling was 4,5 hours.
Under the influence NO -CGF on the cultivated fibroblasts of the skin of man at time 15 sec it was revealed a maximum increase of the synthesis DNA in all sets of experiments on the average by 223,3% in comparison with the control. The number of cells in the Petri dishes after action reliably did not change. With an increase in the exposure of action to 20 sec the synthesis of DNA decreased, comprising in average 65,6% of the control. With the decrease of exposure to 10 and 5 sec the synthesis DNA did not change or insignificantly it was lowered in comparison with the control. The synthesis of protein by fibroblasts also maximally increased with exposure 15 sec - in average 138,5% to the control. After 5 and 10 sec actions it practically did not change (100,7% and 105,7% to the control r espectively).
Under the influence on the fibroblasts by the gas flow of mixture N2 and NO the synthesis of DNA with the exposure 10 and 15 sec it increased practically equally (to 166,0% and 167,5% respectively), and after 20 sec actions it decreased to 118,6% to the control.
Use as the object of the action the cells of neuron of the Gasser's unit of rat revealed the weaker stimulation of synthesis DNA. In this case its maximum increase was determined with exposure 10 sec (121,1%), after 15 sec the synthesis DNA decreased to 110,5%, and after 20 sec - to 102,1% to the control. The synthesis of protein was maximum with fifteen second exposure (152,2%) and was reduced with the decrease of the time of action to 10 sec (98,5%) and its increase to 20 sec (82,2%). The number of cells of neuron in the Petri dishes as fibroblasts, under the effect of the action significantly did not change.
Thus, the obtained results attest to the fact that exogenous NO after the single blowing of the cultures of the fibroblasts of the skin of man and cells of neuron is capable to noticeably strengthen cellular proliferation, increasing synthesis DNA 2,5 times and to a lesser degree (1,5 times) to increase the synthesis of protein by cells. Analogous action is observed also under the influence on the cellular cultures NO- chemical origin, which attests to the fact that the effect is not connected with other factors of the cooled air- plasma flow of apparatus "PLASON".