Medical devices
search
news
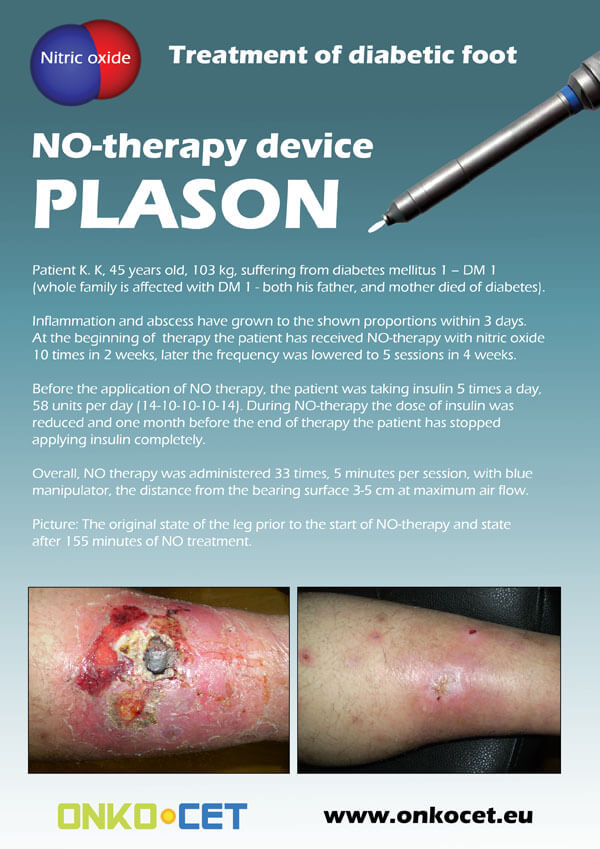
The PDF with the short report with pictures from the therapy of a diabetic foot can be viewed or downloaded here.
The pictures from the treatment of unhealing wounds an be found here:
http://www.onkocet.eu/en/produkty-detail/220/1/
The pictures from the treatment of unhealing wounds an be found here:
http://www.onkocet.eu/en/produkty-detail/293/1/
ONKOCET Ltd. has exhibited the devices from its portfolio on the MEDTEC UK exhibition in Birmingham, April 2011 through our partner Medical & Partners.

 The ONKOCET company has successfully reached the certification of yet another medical device, Infrared Camera SVIT. The Certificate can be found here. The videos from the device operation can be found here.
The ONKOCET company has successfully reached the certification of yet another medical device, Infrared Camera SVIT. The Certificate can be found here. The videos from the device operation can be found here. Our device, the non-invasive blood analyzer AMP has won the Golden Incheba prize at a medical exhibition SLOVMEDICA - NON-HANDICAP 2010. A big thank you goes to the organizers of the exhibition for acknowledging the quality of our device and to the exhibitor, the Medical & Partners company, for introduction of the AMP device to the medical public again.
Our device, the non-invasive blood analyzer AMP has won the Golden Incheba prize at a medical exhibition SLOVMEDICA - NON-HANDICAP 2010. A big thank you goes to the organizers of the exhibition for acknowledging the quality of our device and to the exhibitor, the Medical & Partners company, for introduction of the AMP device to the medical public again.We are pleased to inform our business partners, that our company has succesfully finished the certification process of Concor Soft Contact Lenses.
 You can find the certificate here.
You can find the certificate here.More information on Concor Soft Contact Lenses go to section Medical preparations/Concor soft contact lenses, or follow this link.
 Our company has finished the certification process for another medical device, computerized spirometer MAS-1K with oximeter. You can find the device certificate here.
Our company has finished the certification process for another medical device, computerized spirometer MAS-1K with oximeter. You can find the device certificate here..jpg) Since May 2010 there is a new version of AMP device available.
Since May 2010 there is a new version of AMP device available.Follow this link if you want to see the pictures and specifications of the device.
http://www.onkocet.eu/en/produkty-detail/293/1/
 Dear partners,
Dear partners, In October 2009 we have received CE certificate for another device from our portfolio, NO therapeutical device PLASON. You can find more information about this revolutionary device, used for healing of unhealing wounds, diabetic foot, or for cosmetical purposes, at our webpage, section "Medical devices" -> PLASON-NO Therapy.
.gif)
Best regards
Team of ONKOCET Ltd. company
Sparing coagulation
Sparing coagulation of the wound surfaces
 In a number of cases, when the intensive entering of liquid (for example, the blood or of lymph) from the deep layers of cloth to the surface is absent, it is necessary to conduct partial drying surface in the regime of the sparing coagulation for the purpose of the final evaporation of pathologic liquids (for example, exudate) and achievement of the effect of sterilization.
In a number of cases, when the intensive entering of liquid (for example, the blood or of lymph) from the deep layers of cloth to the surface is absent, it is necessary to conduct partial drying surface in the regime of the sparing coagulation for the purpose of the final evaporation of pathologic liquids (for example, exudate) and achievement of the effect of sterilization.
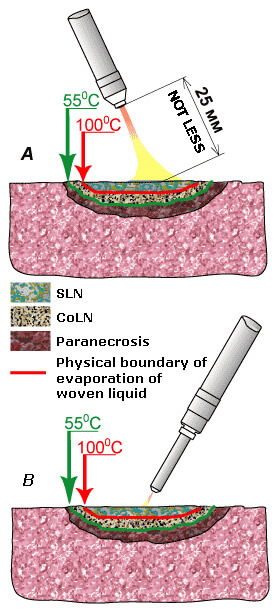
For achievement the effect of partial drying and formulated above tasks there is no need for using entire temperature potential of air-plasma flow (HPF). Sufficient to ensure in the place of the contact of plasma jet with the cloth temperature in the range from 1000°C to 2000°C. The flow charts of the sparing coagulation are shown in the figure.
The sparing coagulation can be carried out as by coagulator (Fig. a), so by stimulator-coagulator (Fig. b). With the use of a coagulator the distance from the outlet to the region of coagulation must be not less than 25 mm. Visually this approximately corresponds to the end of the luminous part of the plasma torch of coagulator. The decrease of distance from the outlet to the region of coagulation will lead to the excess of the temperature limit into 2000°C.
The thermo-physical processes, proceeding during the sparing coagulation, are in many respects similar to the processes, proceeding during the traditional coagulation, but in this case low temperature potential flow does not make possible to be formed for the complete region of thermal changes. Process is limited to the formation of the small zone of spongy necrosis (SLN), zone of compact necrosis (CLN) and zone of paranecrosis. As a result this action the elastic film of lusterless nuance with a thickness not of more than 200 mkm is formed on the surface of cloth, which also is the purpose of the sparing coagulation.
With conducting of the sparing coagulation by stimulator-coagulator the distance from the outlet of manipulator to the cloth is minimal (Fig. b), since the temperature of the escaping flow does not exceed 1000°C.
This way, if it is necessary to realize the sparing coagulations on large surface it is possible to use a coagulator, and if it is necessary to coagulate the bounded spaces - stimulator-coagulator.