Medical devices
search
news
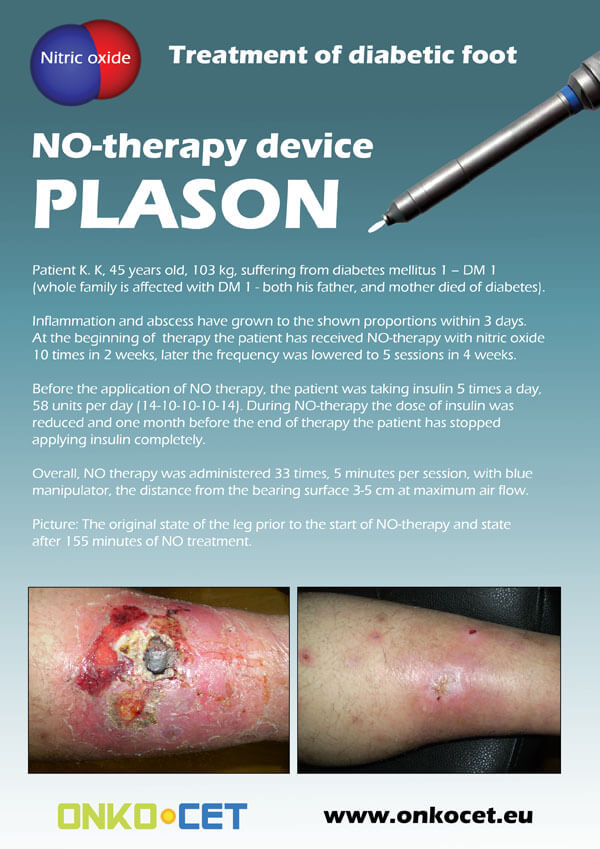
The PDF with the short report with pictures from the therapy of a diabetic foot can be viewed or downloaded here.
The pictures from the treatment of unhealing wounds an be found here:
http://www.onkocet.eu/en/produkty-detail/220/1/
The pictures from the treatment of unhealing wounds an be found here:
http://www.onkocet.eu/en/produkty-detail/293/1/
ONKOCET Ltd. has exhibited the devices from its portfolio on the MEDTEC UK exhibition in Birmingham, April 2011 through our partner Medical & Partners.

 The ONKOCET company has successfully reached the certification of yet another medical device, Infrared Camera SVIT. The Certificate can be found here. The videos from the device operation can be found here.
The ONKOCET company has successfully reached the certification of yet another medical device, Infrared Camera SVIT. The Certificate can be found here. The videos from the device operation can be found here. Our device, the non-invasive blood analyzer AMP has won the Golden Incheba prize at a medical exhibition SLOVMEDICA - NON-HANDICAP 2010. A big thank you goes to the organizers of the exhibition for acknowledging the quality of our device and to the exhibitor, the Medical & Partners company, for introduction of the AMP device to the medical public again.
Our device, the non-invasive blood analyzer AMP has won the Golden Incheba prize at a medical exhibition SLOVMEDICA - NON-HANDICAP 2010. A big thank you goes to the organizers of the exhibition for acknowledging the quality of our device and to the exhibitor, the Medical & Partners company, for introduction of the AMP device to the medical public again.We are pleased to inform our business partners, that our company has succesfully finished the certification process of Concor Soft Contact Lenses.
 You can find the certificate here.
You can find the certificate here.More information on Concor Soft Contact Lenses go to section Medical preparations/Concor soft contact lenses, or follow this link.
 Our company has finished the certification process for another medical device, computerized spirometer MAS-1K with oximeter. You can find the device certificate here.
Our company has finished the certification process for another medical device, computerized spirometer MAS-1K with oximeter. You can find the device certificate here..jpg) Since May 2010 there is a new version of AMP device available.
Since May 2010 there is a new version of AMP device available.Follow this link if you want to see the pictures and specifications of the device.
http://www.onkocet.eu/en/produkty-detail/293/1/
 Dear partners,
Dear partners, In October 2009 we have received CE certificate for another device from our portfolio, NO therapeutical device PLASON. You can find more information about this revolutionary device, used for healing of unhealing wounds, diabetic foot, or for cosmetical purposes, at our webpage, section "Medical devices" -> PLASON-NO Therapy.
.gif)
Best regards
Team of ONKOCET Ltd. company
Treatment of wounds, patients with cancer
Application of an apparatus “PLASON” in the treatment of wounds, wound and beam pathology by oncologic patients
Higher risk of the development of postoperative complications (wound infection, the prolongedly unhealing wounds and other) by oncologic patients - 74,1% against 25,9% of patients, who did not have oncologic disease is convincingly shown in the classical work of E. Lohde with co-auth. (1993). The frequency of complications is connected with the following factors:
- operational interference are carried out under the conditions of aggressive radio-chemotherapy, which worsens the local and system mechanisms of the regulation of reparative processes;
- conducting plastic-reconstruction operations is frequently accompanied by the connection of different, including artificial, organs and tissues, which under the conditions for immunodepression, disturbances of lympho- and haematokinetics lead to the development of the early or distant complications;
- the majority of operational surgery in oncology is carried out under the initially infected conditions or they are accompanied by the expiration of the aggressive media, additionally traumatizing the remaining cloths and increasing the high forecast of development of different complications.
Under these conditions noted in the previous sections of these work, the regulating and biostimulating properties of exogenous NO seem to be especially promising.
In MNIOI of P. A. Gertsen for treating of postoperative wounds and intra-operating action “Gemoplaz VP” apparatus was used since 1997, and from 1999 the apparatus “PLASON”. Two groups of oncologic patients were isolated, by whom the treatment by air- plasma flows and by the nitrogen oxide was carried out.
The first group composed of 350 patients at the age of 18-73 years, where NO-therapy of wounds was used in connection with the postoperative complications, which were developed as a result of the surgical treatment apropos of the tumors of different localizations.
Until the operation the radiation therapy was carried out by 168, and chemotherapy by 66 to patients.
The removal of tumor with the plastic closing of defect was carried out to all patients in the stage of surgical treatment. In this case they have used dermal transplants, skin-facial, muscular and osteomuscular rags in free version as well as displaced on the leg. Postoperative complications were in essence the open defects of cloths both with the remainders of the reseated derma (147 patients) and without it (140 patients).
Nature of the postoperative complications
Nature of the complication | Quantity of the patients |
Defect of cloths with the remainders of the reseated derma | 147 |
Diastasis of the postoperative wound | 28 |
Diastasis of postoperative wound + the blowhole | 21 |
Open defect of the cloths | 140 |
Blowhole | 14 |
Summary | 350 |
The treatment of wound surface by gas flow in the regime of NO-therapy was conducted daily, 10 times in the average. The time of working (from 30 s to 3 min) depended on the size of wound defect. Sterile napkin was superimposed after each procedure on superficial wound and wound they conducted dryly. The effectiveness evaluation criteria for exogenous NO-therapy in this group were the dynamics of inflammatory process, the forming of granulating cloth and epithelization. Clinical effect was evaluated to the end of the course of NO-therapy (from 1 to 3 weeks). In the part of the group of patients a histological and histochemical study of bioptat from the edge of wound was carried out prior to the beginning and in the process of treatment.
The second group was formed by 85 oncologic patients, by whom the action APF in the regime of coagulation was conducted intra-operating. By the purpose of the air- plasma coagulation of wound surface was the decrease of the volume of intra- and postoperative diffuse roof and plasma losses, increase in ablate by creating the thin coagulation shaft for the blockade of lymphatic slots and capillaries, the decrease of postoperative complications. The effectiveness evaluation criteria for this form of action were the volume of intra- and postoperative diffuse roof and plasma losses, number of developed postoperative complications and relapses of tumor. In the postoperative period the NO- therapy was carried out.
As a result treatment in the 1st group the inflammatory process is liquidated with the complete healing of wound and (or) by closing blowhole, by 91 (26%) patients, by 238 (68%) patients the decrease of the degree of inflammatory manifestations is noted, by 21 (6%) patients positive effect was absent. They were sluggish prior to the beginning of treatment in 68% of cases (238 patients) of granulation in the wound, by 26% (91 patients) - moderated and only in 6% of cases (21 patients) - active. As a result of NO- therapy by 329 (94%) patients was noted the growth of active granulating cloth, by 14 (4%) patients - granulating cloth was represented moderately and by 7 (2%) patients the nature of granulating cloth remained sluggish. On the average after 2-3 procedures the making more active of an increase in the granulating cloth was already noted, i.e., the flow of the first phase of wound process (stage of inflammation) was accelerated, it began more rapidly and the stage of regeneration flowed more actively.
The process of epithelization prior to the beginning of NO- therapy was expressed only by 42 (12%) patients, after its conducting - by 308 (88%). At the moment of the beginning of NO- therapy of 245 patients, with which the transplantation of derma was produced (separately or in combination with other forms of plastic material), the complete lysis of the reseated derma was noted by 98, partial - by 133 and beginning lysis- by 14 patients. After conducting of NO- therapy by all patients was expressed the process of the epithelization either in the form of the making more active of the preserved centers of the reseated derma in the case of its partial lysis or in the form of boundary epithelization. By 133 patients from this group islet epithelization was noted. By 7 patients the islet epithelization was noted in the section of the reseated muscle (without the derma).
State of the reseated derma before and after of the beginning of the NO- therapy
Before NO-therapy | After NO-therapy | Quantity of the patients |
Beginning of the lysis | Activation of the reseated derma + the islet epithelization | 7 |
Beginning of the lysis | Activation of the reseated derma | 7 |
Partial lysis | Activation of the reseated derma + the islet epithelization | 77 |
Partial lysis | Activation of the reseated derma | 56 |
Complete lysis | Boundary epithelization | 49 |
Complete lysis | Boundary + islet epithelization | 49 |
Summary |
| 245 |
With an histological and histochemical study of bioptat of the complicated prolongedly unhealing live wounds immediately after of the first session of NO- therapy the dilation of micro-vessels, the decrease of the intravascular sludging of erythrocytes was noted. Through 4-6 sessions a significant decrease or the disappearance of the signs of the microcirculatory disturbances very expressed in initial bioptats was revealed: micro-dusts devil, sludge of erythrocytes, aggregation of thrombocytes, "closed foci "of leukocytes, vasculitis, the destruction of endothelium, contraction and obliteration of opening. Microbial sowing considerably decreased or disappeared, the phagocytic activity of neutrophils and macrophages with respect to the bacteria and the necrotic detrite was strengthened, the purification of wound from the fibrinopurulent exudate and the detrite occurred. The inflammatory manifestations were sharply descended: the permeability of the walls of micro-vessels, edema, neutrophilic infiltration. Dystrophic and necrotic changes in the cells and cloths decreased, the reaction of fat cells, macrophage reaction, macrophage- fibroblastic interaction, proliferation of fibroblasts and new formation of capillaries was strengthened. The granulating cloth with the vertical vessels was formed, which then ripened and underwent the fibrocicatricial transformation (maintenance of cells and vessels it decreased, and it increased collagenic fibers).
In the 2nd group by all patients, to whom the intra-operating air- plasma treatment of operating wound in the regime of coagulation was conducted before its closing by plastic material, it was possible to create thin coagulation film on entire perimeter and areas of wound during 1 min of action, which is considerably more rapid than with the traditional electrocoagulation. Decrease 2 times in comparison with the usual method of diffuse roof and plasma losses in the early postoperative period was noted. Postoperative complications in this group of patients were not observed.
A histological and histochemical study of bioptats from the different sections of wound showed that through several minutes after action of APF on superficial wound thin (200-600 microns) layer of the coagulated cloth is formed. Cellular elements in this layer are necrotized, the openings of vessels are thrombosed. Under the layer of the coagulation necrosis of strengthening inflammatory changes in cloth and increases in the number of muscular fibers and cells in the state they did not reveal destruction.
NO- therapy was used also for treating the early and late beam reactions - moist epidermis, dry epidermis, dry epidermis in combination with stomatitis, vulvitis, phlebitis, beam fibrosis, that became the reason for interruption in conducting of the radiation therapy. As a result NO- therapy early beam reactions were cured in 88% of patients within the maximally compressed periods (in 2-5 days), which made it possible to renew the radiation therapy. With the expressed beam fibrosis of the skin, subcutaneous fatty cellular tissue and cellulose tissue of small basin, that were developed after chemo-radio treatment, after 2 courses of NO- therapy (course on 8-10 sessions with the interruption in 2-3 weeks) is noted the expressed positive dynamics in the form of the decrease of sizes and density of fibrous cloth, normalization of color, sensitivity and turgor of the skin, increase of the volume of motions in the hip joints and the normalization of the function of urinary system, decrease or total curtailment of painful syndrome. For the purpose of the study of the nature of blood flow in the focuses of fibrosis by this patient was carried out an Doppler- ultrasonic study of the vessels before and after of the session of NO- therapy. Was noted strengthening blood flow both due to the increase in the diameter of vessels and due to the discovery of backup capillaries, in the arterioles and venules. An histological and histochemical study of bioptats of the skin after 10-15 sessions of NO- therapy in contrast to the initial demonstrated the significant normalization of microcirculation and structure of the collagenic fibers of derma, the absence of hyalinosis and fibrinoid, an increase in the content of acid glycosaminoglycans in the matrix of cloth and RNA in the cytoplasm of fibroblasts, the decrease of vasculitis and dystrophy of epidermis.
Thus, the experience of the use of an apparatus “PLASON” in oncology showed that the intra-operating working in the regime of coagulation ensures ablasticyte, considerable decrease of plasma and blood losses from the extensive wound surfaces as a result of shaping of the thin film of the coagulation necrosis of cloth. At the NO- therapy of the complicated postoperative wounds is achieved decrease or the liquidation of inflammatory process, the stimulation of the development of granulating cloth and the acceleration of epithelization. Effect begins independent of localization of wounds on the tele-, and also the version of plastic material. The positive side of method is also the preventive maintenance of the local relapses of tumor, which makes possible its wider application in the oncoplastic surgery. The effectiveness of NO- therapy during the treatment of early beam reactions makes it possible in 88% of patients to carry out the valuable course of the radiation therapy. Treatment of the beam fibroses of cloths gives the expressed therapeutic effect.