Medical devices
search
news
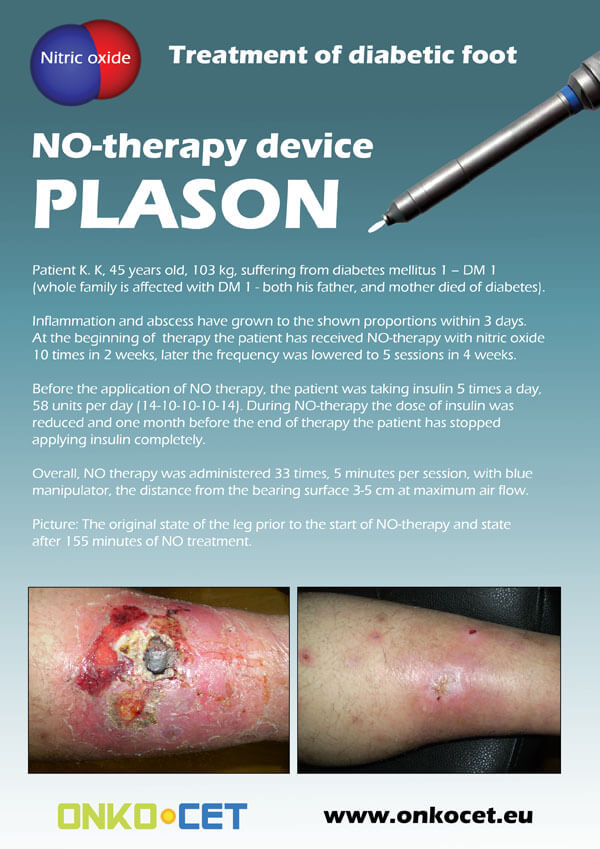
The PDF with the short report with pictures from the therapy of a diabetic foot can be viewed or downloaded here.
The pictures from the treatment of unhealing wounds an be found here:
http://www.onkocet.eu/en/produkty-detail/220/1/
The pictures from the treatment of unhealing wounds an be found here:
http://www.onkocet.eu/en/produkty-detail/293/1/
ONKOCET Ltd. has exhibited the devices from its portfolio on the MEDTEC UK exhibition in Birmingham, April 2011 through our partner Medical & Partners.

 The ONKOCET company has successfully reached the certification of yet another medical device, Infrared Camera SVIT. The Certificate can be found here. The videos from the device operation can be found here.
The ONKOCET company has successfully reached the certification of yet another medical device, Infrared Camera SVIT. The Certificate can be found here. The videos from the device operation can be found here. Our device, the non-invasive blood analyzer AMP has won the Golden Incheba prize at a medical exhibition SLOVMEDICA - NON-HANDICAP 2010. A big thank you goes to the organizers of the exhibition for acknowledging the quality of our device and to the exhibitor, the Medical & Partners company, for introduction of the AMP device to the medical public again.
Our device, the non-invasive blood analyzer AMP has won the Golden Incheba prize at a medical exhibition SLOVMEDICA - NON-HANDICAP 2010. A big thank you goes to the organizers of the exhibition for acknowledging the quality of our device and to the exhibitor, the Medical & Partners company, for introduction of the AMP device to the medical public again.We are pleased to inform our business partners, that our company has succesfully finished the certification process of Concor Soft Contact Lenses.
 You can find the certificate here.
You can find the certificate here.More information on Concor Soft Contact Lenses go to section Medical preparations/Concor soft contact lenses, or follow this link.
 Our company has finished the certification process for another medical device, computerized spirometer MAS-1K with oximeter. You can find the device certificate here.
Our company has finished the certification process for another medical device, computerized spirometer MAS-1K with oximeter. You can find the device certificate here..jpg) Since May 2010 there is a new version of AMP device available.
Since May 2010 there is a new version of AMP device available.Follow this link if you want to see the pictures and specifications of the device.
http://www.onkocet.eu/en/produkty-detail/293/1/
 Dear partners,
Dear partners, In October 2009 we have received CE certificate for another device from our portfolio, NO therapeutical device PLASON. You can find more information about this revolutionary device, used for healing of unhealing wounds, diabetic foot, or for cosmetical purposes, at our webpage, section "Medical devices" -> PLASON-NO Therapy.
.gif)
Best regards
Team of ONKOCET Ltd. company
Diagnostic significance
Diagnostic significance
In accordance with in force standard on the spirometry, the developed together American thoracic society and the European respiratory society (ATS/ERS 2005), the results of spirometric study will be diagnostically meant with satisfaction of the following basic conditions:
- three technically acceptable attempts must be executed;
- the values of the indices FER, measured in these attempts, must be reproduced.
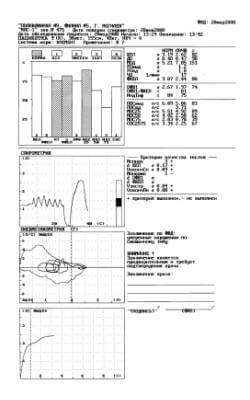
Fig. 1. Protocol of a study with the first attempt.
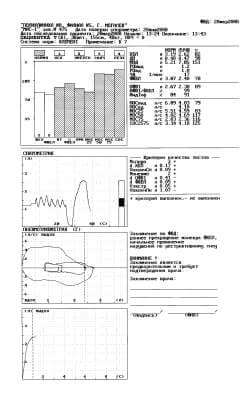
Fig. 2. Protocol of a study with the second attempt.
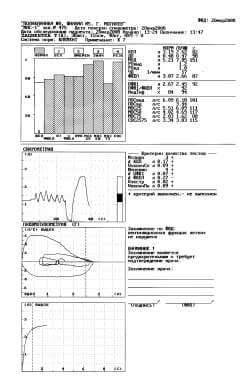
Fig. 3. Protocol of a study with the fourth attempt.
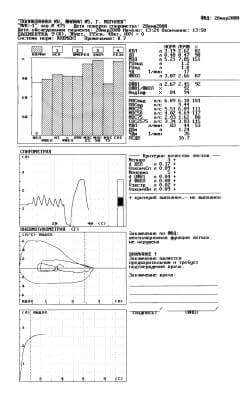
Fig. 4. Protocol of a study with the fifth attempt.
Based on the example of conducting the study of FER, executed with the patient N, we will illustrate the importance of satisfaction of the conditions mentioned above.
The first protocol of the study, carried out on the spirometer MAS-1, is represented in figure 1.
Let us note that the spirometer MAS-1 in accordance with ATS/ERS 2005 it measures and calculates besides the parameters of FER the following parameters of the technical acceptability of the tests:
- VfinSp - characterizes the completeness of the completion of expiration in the maneuver VC;
- Vextr - characterizes the effort of patient at the beginning of the forced expiration;
- VfinPn - characterizes the completeness of the completion of expiration in the maneuver FVC.
and also the parameters of reproducibility of the tests:
- dVC - reproducibility VC (maneuver VC);
- dFEV1 - reproducibility FEV1 (maneuver );
- dFVC - reproducibility FVC (maneuver FVC).
Furthermore, instrument informs about a quantity of attempts, executed in the maneuvers VC (Nspiro) and FVC (Npneumo).
Thus, the purpose of conducting a spirometric study is reaching the diagnostically significant and reproducible studies of FER, about than the instrument informs by sign “+” in the appropriate criterion of the quality of tests. As is evident in figure 1, the first protocol of the study FER informs about a reliable study in the spirometry Nspiro “+” (3 attempts), dVC “+” and about the fulfillment of one (Npneumo = 1, “-”) technically acceptable attempt in the maneuver FVC (Vextr = 0,04 l, “+”, VfinPn = 0,08 l, “+”). The conclusion of instrument “moderate disturbances according to the mixed type” - are reduced both the volumetric (VC, FVC) and high-speed (FEV1, MEF 50, MEF 75, FEF 25-75) indices of pulmonary ventilation. Let us note that the patient carried out spirometry for the first time.
With conducting of the second attempt (Fig. 2) we see the already more adequate performance of maneuver FVC: FEV1 grew from 1,97 l to 2,38 l - patient, being trained, made more energetic expiration. Problematic are early curtailment of expiration (duration of expiration ~ 1,2 s, VfinPn = 1,07 l, “-”), and also insufficient reproducibility FEV1 (0,41 l, “-”). Therefore should be carried out still one attempt in the test FVC.
Let us note that the more energetic accomplishment of maneuver FVC led to the normalization of high-speed indices FER (corresponding columns in the diagram they were shaded), and conclusion fixes only the “initial manifestation of disturbances according to the restrictive type”. Finally, in the 4th (Fig. 3) to technically acceptable attempt (Vextr = 0,02 l, “+”, VfinPn = 0,09 l, “+”) we obtain required reproducibility FEV1 (dFEV1 = 0,07 l, “+”), and FVC grows from 2,40 l to 2,66 l and composes 87% with respect to the proper it, i.e., corresponds to standard.
In the 5th attempt (Fig. 4) is reached reproducibility FVC (dFVC = 0,08 l, “+”), that can be treated as the correct completion of test FVC. Conclusion of the spirometer: “the ventilation function of lungs is not disrupted”.
Thus:
- FEV1 with 1,97 l in the 1st attempt grew to 2,38 l in the 2nd (+ 21%) and to 2,45 l in the 4th attempts (+ 24%);
- FVC with 2,40 l in the 2nd attempt (decrease connected with the short expiration - VfinPn = 1,07 l, “-”) grew to 2,66 l in the 5th attempt (+ 11%);
- FEV1/FVC with 81% in the 1st attempt grew to 92% in the 4th (+ 11%).
Thus, if we carried out only one attempt in the pneumo-tachometry, and often then it occurs in the practice of functional diagnostics, then in the patient would be “moderate disturbances according to the mixed type”. The following (2nd) attempt with the more energetic expiration leads to the removal of obstruction, and in the patient of altogether only the “initial manifestation of disturbances according to the restrictive type”.
Finally, the 4th attempt with the technically acceptable (more complete) completion of expiration (VfinPn = 0,09 l, “+”) makes it possible to remove initial restriction, giving the conclusion: “the ventilation function of lungs is not disrupted”.
It should be noted that in patients, who regularly carry out spirometry, such spreads of respiratory maneuvers they are encountered more rarely; however, in this case the expert system of spirometer MAS-1, which calculates the criteria of technical acceptability and reproducibility of tests, it makes it possible completely to clearly divide the objective spirometry (maximum quantity “+” in the criteria of the quality of tests), which gives the diagnostically significant results, from the spirometry, executed not in accordance with the standards (significant quantity “-” in the criteria of the quality of tests). Last situation can appear with conducting of studies by insufficiently experienced personnel, and also with the examination of the ability to work/of the disablement, when it is necessary to objectively prove the cases of possible simulation that also makes it possible to make protocol of the study FER of the spirometer MAS-1 on the basis of the criteria values of quality tests.
When the protocol of a study does not contain information about quality and completeness of the carried out tests, to doctor, who interprets spirogram, to there remains only hope for honesty and competence of the medical staff (its clinic or any other, from where it was directed patient), which conducted the study of FER.
Diagnostic significance
In accordance with in force standard on the spirometry, the developed together American thoracic society and the European respiratory society (ATS/ERS 2005), the results of spirometric study will be diagnostically meant with satisfaction of the following basic conditions:




When the protocol of a study does not contain information about quality and completeness of the carried out tests, to doctor, who interprets spirogram, to there remains only hope for honesty and competence of the medical staff (its clinic or any other, from where it was directed patient), which conducted the study of FER.